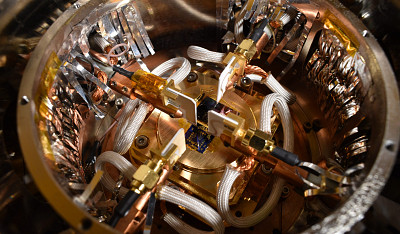
Researchers from the Nanocenter at the Jožef Stefan Institute in Ljubljana, in collaboration with Google’s Quantum AI lab, are developing a new generation of quantum chips that promise enhanced stability and efficiency for quantum computers. The project focuses on improving the stability of quantum bits (qubits), the fundamental building blocks of quantum computing, whose reliable performance is crucial for further technological progress in the field.
At the core of the research is the use of a layered material, tantalum disulfide, which enables the creation and precise control of quantum states through electrical pulses. This represents a significant step toward the development of practical quantum electronic components.
The project is taking place during the year declared by the United Nations General Assembly as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology, further emphasizing the global importance of research in this rapidly evolving domain.
You can read more in the original article published on STAznanost: Slovenian Laboratory Collaborates with Google to Develop Technology for a New Generation of More Stable Quantum Chips.